Gum disease is the most prevalent dental problem affecting people of all age groups globally. This is a leading cause of tooth loss when left untreated.
The dental practice in Indianapolis offers comprehensive evaluation and treatment of periodontal disease to improve your overall dental health.
What is periodontal disease?
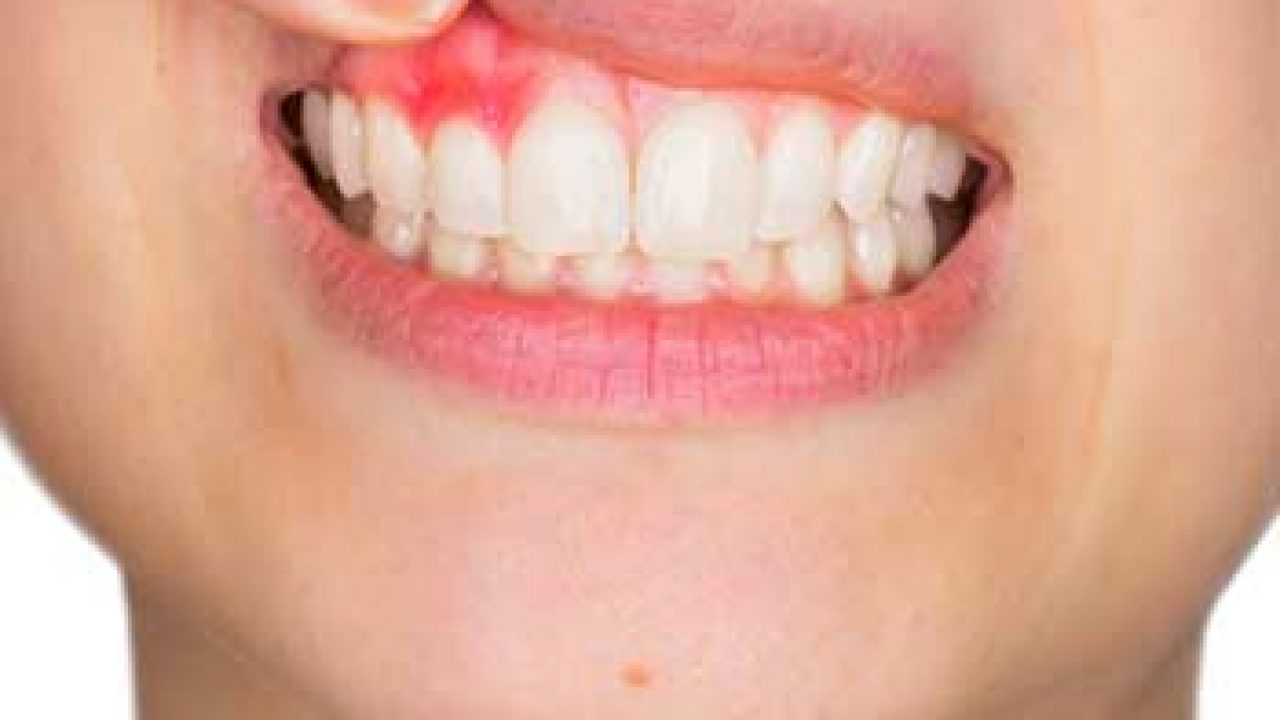
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition affecting the soft tissues surrounding your teeth. This comprises the gums that encircle the teeth, providing support. It is characterized by an infection or inflammation of the gums, leading to a series of clinical signs and symptoms.
Gum disease is reversible in the early stage, but when left untreated, the infection can invade the underlying alveolar bone, leading to periodontitis. This is the most common cause of tooth loss.
What are the types of periodontal disease?
Gum disease can be classified into different forms based on the severity of the infection. These include:
- Gingivitis
- Chronic periodontitis
- Aggressive periodontitis
- Necrotizing periodontitis
- Periodontitis caused by systemic disease
What are the possible causes of periodontal disease?
The buildup of excess plaque is the prime concern that leads to bacterial colonization. These microorganisms release harmful toxins that damage the soft tissues. An alteration in your immune system also causes failure to fight against infections.
Gum disease is likely to develop due to the following risk factors:
- Genetic predisposition
- Poor oral hygiene
- Pregnancy and menopause due to hormonal changes
- Tobacco use
- Smoking
- Stress
- Obesity (being overweight)
- Certain autoimmune diseases like lupus
- Heart or respiratory disease
What are the clinical features of periodontal disease?
The most striking feature of periodontal disease is bleeding gums while brushing or flossing.
Other clinical symptoms include:
- Reddish purple gums
- Swollen and tender gums
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Unpleasant taste
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Malalignment that can lead to more plaque accumulation
How is periodontal disease treated?
The ideal treatment recommended depends on the severity of the periodontal disease.
Treatment options include:
- Scaling and root planing
- Professional dental cleaning once every 6 months can prevent plaque formation.
- It also helps to detect early signs of gum disease and halt the disease progression.
- Tissue regeneration
- This treatment encourages the growth of gum tissues through grafting.
- A biocompatible layer or membrane is inserted into the affected area to promote regeneration of the tissues.
- Pocket elimination surgery
- This is a flap surgery that reduces the size of the gingival pocket between the gums and the teeth.
- Dental implants
- Loss of teeth due to periodontal disease can be effectively replaced using dental implants.
- These act as an anchorage for crown placement.
Remember, proper oral hygiene practice is the key to keeping gum disease at bay and also to maintain the results of any periodontal treatment for years to come.